Project "Dissemination of innovations in the Sahelian zone (DISSEM-INN)"
Last update: 13 March 2024
Project presentation
Funded by AFD and coordinated by CIRAD, the DISSEM-INN project concerns a set of eight projects* launched under the EU initiative Development Smart Innovation through Research in Agriculture (DeSIRA) and implemented in the Sahel.
These projects contribute to the development of sustainable agri-food systems that are resilient to climate change by focusing on innovation process, each in a specific field. These projects are: ABEE, ACCEPT, APSAN-Mali, BIOSTAR, CASSECS,FAIR, IRRINN and S&T.
The knowledge gained by these projects through the implementation of their innovations is a valuable source of information. The "Dissemination of innovations in the Sahelian zone (DISSEM-INN)" project aims to capitalize on this experience in order to enable these projects to share their achievements for mutual benefit and to transfer this knowledge to other actors engaged in similar initiatives.
To this end, DISSEM-INN is working with the DeSIRAs involved to establish multi-stakeholder dialogue forums. These forums will enable the co-construction of a cross-cutting analysis of these innovation process, the methodologies used to implement them and their dissemination and adoption strategies. Thanks to this cross-cutting framework, levers will be identified to support their deployment on a larger scale.
The characteristics of the eight DeSIRAs involved
Geographical distribution
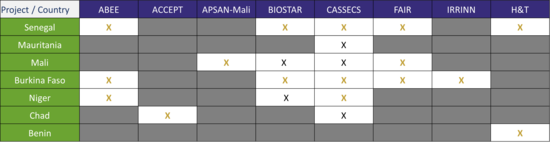
The first common characteristic of these DeSIRA projects is their geographical proximity (see Figure 1 below), since they are all implemented in the Sahel region, and therefore target relatively similar ecological zones and types of agriculture. For this reason, they share common challenges, including: very high population growth, extreme poverty (approximatively 50% of the population), high climate risks (a sharp increase in temperatures combined with soil degradation, which could reduce agriculture yields by 50%), and an increase in violent conflicts.
Figure 1 illustrating the geographical distribution of the eight DeSIRA projects involved
Thematic distribution
The projects are also characterised by the fact that they address Sahelian issues by focusing on sustainable agriculture and food security. They are therefore grouped around five key themes (see Figure 2 below) to pursue their common goal: varietal improvement, agroecology, livestock, bioenergy, and irrigation.
Figure 2 illustrating the thematic distribution of the eight DeSIRA projects involved
* Originally, the DISSEM-INN project involved a total of nine DeSIRA projects, including INV-Niger, but due to the discontinuation of its activities, DISSEM-INN has capitalized on only eight projects since 2023.
Last update: 13 March 2024